Mapping a Route to Successful Automation Implementation
Have you noticed how the solution to most problems these days seems to be technology? Our lives are intertwined and interconnected in ways that few could have imagined several decades ago. From smart phones and televisions to smart cars and thermostats, advanced technologies that communicate and share information via the Internet have changed our lives forever.
They’ve also changed our workplaces. You’d expect this working in a technology field, but even industrial factory jobs have been impacted greatly by today’s advanced automation technologies. Just like in every other area of our lives, technology has changed the modern industrial workplace forever.
The seismic effect advanced automation technologies have had on manufacturing and other industrial sectors has many monikers, many of which you’ve probably heard of: the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and Smart Factory are just a few.
Especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, today’s industries know that they need to invest in advanced automation technologies to take them to the next level of efficiency and productivity. Yet, these investments should not be made lightly, especially by small and medium-sized manufacturers that don’t have the kind of money to spend that huge multinational corporations do.
How should small and medium-sized manufacturers approach investing in new automation technologies? In a recent IndustryWeek article, author Robert Scipione provides some guidance, including this important starting point: “The most important aspect of your first automation project is to be clear about what problem you are trying to solve.”
Failure to address a specific goal is a recipe for disaster. Scipione notes that some manufacturers buy technology impulsively, but “if they haven’t considered all the related impacts on their people and processes, their chances of a successful automation implementation are diminished.”
Once a problem is identified, Scipione recommends tying “the initiative to financial performance” and then “build[ing] a system around the technology.” In this way, you can ensure smooth implementation while also tracking how your chosen automation solution saves money and provides a good return on investment.
While many might be tempted to focus on the technology options available as potential solutions, Scipione warns that current personnel must also be a big part of the equation: “you will want to factor your people and their skill sets into the automation implementation, operation, and support.”
Technology doesn’t exist in a vacuum, so it’s important to ensure skilled personnel are available to operate, maintain, troubleshoot, and repair these new technologies as implemented. In many cases, that will mean either upskilling current workers or hiring new workers with the advanced automation technology skills you require.
If hiring new workers ends up being part of your automation implementation plan, look for candidates with industry-standard credentials that prove they already possess the advanced automation skills needed to thrive. For example, if workers possess a certification from the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), employers can feel confident they’ve already proven they have the knowledge and hands-on skills needed for working with advanced smart automation technologies. SACA has been hard at work collaborating with industry leaders to develop a wide variety of industry-standard certifications that will help employers find workers who possess the advanced connected-systems skills they need to take their businesses to the next level. Be sure to check out SACA and all it has to offer!
- Published in News
Scottish Candy Maker Using Automation to Find the Sweet Spot
When the holidays roll around, do you find yourself yearning for homemade treats your mother, grandmother, or favorite aunt made when you were a kid? There’s simply nothing like cookies or fudge made from a recipe that’s been handed down for years from one generation to another.
Of course, most people won’t turn away sweet treats from the store either. In fact, many of your favorites might come from confectioners who have been making signature candies for decades using handmade recipes created by their founders long ago.
That’s certainly the case with Aldomak, a family-run Scottish confectioner with a factory in Glasgow. A recent article in The Manufacturer notes that “[t]he confectioner prides itself on its handmade recipes.” However, like most other factories in this modern age, Aldomak is “gradually integrating a degree of automation into production processes.”
While priding itself on its traditions, the family that runs Aldomak realized that incorporating some new advanced automation technologies could help them “streamline manufacturing processes and increase capacity.” That’s why they created “a digital simulation of Aldomak’s fudge production line” with the help of “the National Manufacturing Institute Scotland (NMIS) – operated by the University of Strathclyde and part of the High Value Manufacturing (HVM) Catapult.”
Using this digital twin of a production line, “Aldomak and the Design Engineering team at NMIS identified potential bottlenecks and explored various ‘what-if’ scenarios, such as adding new equipment or modifying workflows.” For example, “[b]y examining the capacity of boiling equipment and the movement of both personnel and products within the factory, Aldomak established how best to focus its efforts to boost efficiency.”
Like all advanced automation technologies, the digital twin used by Aldomak relies heavily on a wide range of data, including “the capacity of the machinery, the duration of different cycles, inventory levels and work schedules.” Analyzing this data has “encouraged the manufacturer to think differently, focus on bottlenecks, and explore various ways to increase throughput before considering major investments.”
Gwenole Henry, Research & Development Engineer at NMIS, points out that “[d]igital simulations of this kind can be an incredibly useful tool for manufacturers in any sector, helping them to meet goals and ambitions in terms of productivity, sales and even energy efficiency.”
However, advanced automation technologies like digital twins don’t exist in a vacuum. It’s important to ensure skilled personnel are available to operate, maintain, troubleshoot, and repair these new technologies as implemented. In many cases, that will mean either upskilling current workers or hiring new workers with the advanced automation technology skills you require.
If hiring new workers ends up being part of your automation implementation plan, look for candidates with industry-standard credentials that prove they already possess the advanced automation skills needed to thrive. For example, if workers possess a certification from the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), employers can feel confident they’ve already proven they have the knowledge and hands-on skills needed for working with advanced smart automation technologies. SACA has been hard at work collaborating with industry leaders to develop a wide variety of industry-standard certifications that will help employers find workers who possess the advanced connected-systems skills they need to take their businesses to the next level. Be sure to check out SACA and all it has to offer!
- Published in News
Condition Monitoring Offers Cost-Effective Entry into World of Industry 4.0
According to a recent IoT For All article by Brian Harrison, “[t]he factory of the future, in which all conceivable devices are connected with their intelligence and autonomy and each plant process is constantly optimized through sophisticated real-time analytics, has long been the utopia of industrial automation.”
After all, what manufacturer doesn’t want to be as efficient and productive as possible? Harrison notes that these new advanced automation technologies “promise to unlock unseen levels of productivity and efficiency while removing the need for humans to carry out many of the more repetitive or labor-intensive tasks required, potentially saving organizations vast amounts of money and time.”
However, all you have to do is look at the current state of modern manufacturing to know that “the idea of the smart factory is not yet a reality for all.” While many manufacturers have embraced new automation technologies, others have yet to do so, citing both the cost of technology and inability to hire skilled workers that know how to use these technologies as reasons.
Harrison acknowledges that “[i]t takes time, planning, and often significant investment to radically modernize an entire plant from the ground up.” But maybe “a radical rebuild is not necessary to start embracing the benefits of Industry 4.0.”
What if, instead, manufacturers started small and built up their capabilities over time? According to Harrison, “[i]ncremental improvements, such as adding condition monitoring capabilities to existing equipment can unlock a vast potential for savings across the areas of efficiency, productivity, and reliability throughout the plant.”
The author argues that manufacturers “can implement condition monitoring without substantially rethinking existing processes, and you can roll it out on a much smaller scale to embrace the efficiency, reliability, and productivity savings promised by Industry 4.0, at a fraction of the cost.”
Doing so “offers greater visibility over running processes. Digital connectivity provides real-time or near-real-time insight into asset health, allowing maintenance teams to focus their efforts where needed and avoid expending resources unnecessarily. It can also prevent large amounts of downtime by flagging and fixing potential issues before they turn into failures.”
Harrison urges manufacturers to “[a]ttach sensors to legacy equipment to measure health, tracking metrics like vibration, temperature, and power signatures for a comprehensive view, avoiding manual component inspection. Measuring and analyzing assets remotely improves plant safety in hazardous areas without endangering personnel.”
Incorporating condition monitoring into manufacturing processes allows manufacturers to transition from reactive maintenance to predictive maintenance. Over time, manufacturers can add more technologies, such as manufacturing execution systems and enterprise asset management systems to more thoroughly take advantage of data being collected.
Harrison concludes that “condition monitoring enables companies to start small, and grow digital capabilities gradually in a more manageable and cost-effective way. This also allows you to prioritize assets in a way that provides the best return on investment. From there, you can expand condition monitoring programs to other operations, and before you know it, much of the plant will be connected.”
Of course, part of the transition to Industry 4.0 has to be upskilling current workers and/or hiring new workers with the skills necessary to operate, maintain, troubleshoot, and repair a wide variety of advanced automation systems. How can manufacturers accomplish this?
Today, more and more employers are looking for workers with industry-standard certifications that prove they have the skills needed. For example, if workers possess a certification from the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), employers can feel confident they’ve already proven they have the knowledge and hands-on skills needed for working with advanced smart automation technologies. SACA has been hard at work collaborating with industry leaders to develop a wide variety of industry-standard certifications that will help employers find workers who possess the advanced connected-systems skills they need to take their businesses to the next level. Be sure to check out SACA and all it has to offer!
- Published in News
Automation and the Skills Gap: Hiring for the Present and the Future
Looking to add a highly skilled automation engineer to your company? Finding one may be more difficult than you anticipate—and not for the reason you might think. Although highly skilled workers of all kinds appear to be in short supply these days, the real problem may lie in how employers are communicating their needs to potential workers.
According to a recent IndustryWeek article by Ryan Secard, “[s]killed job candidates say it’s taking longer to find work, despite huge numbers of open positions in manufacturing, because hiring companies either don’t know what they want or can’t explain it to candidates.”
Could ineffective communication be responsible for making the skills gap even wider? According to Secard, “employers appear to be leaving a gap in the market between the open jobs they say they need to fill and how they’re explaining those opportunities to people seeking new positions.” Moreover, “[t]he issue companies are having with anticipating needed skills…is thanks to automation.”
For example, take a look at a common position many companies need to hire for on a regular basis: maintenance technician. Pretty straightforward, right? Not in today’s automated industrial world! As advanced automation technologies proliferate in the workplace, employers are left to guess about the future. Will they need more or fewer employees down the road? More importantly, what skills will their maintenance technicians need in six, twelve, or eighteen months from now?
Compounding these issues is the fact that more than half of job seekers in a recent survey indicated that they believed “a lack of skills is holding [them] back from finding meaningful employment.” Again, communication could be key, as many job seekers report that job descriptions “often include unrealistic minimum qualifications for relatively low positions.”
What can companies do to improve their communications with potential workers and begin filling the open positions they have? First, they must focus on developing a better understanding of the skills they need to hire for. With so many “job candidates confused and depressed,” “the onus is on companies to articulate the skills they’re looking for.”
Secard’s article notes a couple of approaches companies can take. For example, he points out Siemens AG’s focus on mechatronics skills to find versatile engineers. The idea is that “[a]n engineer trained in mechatronics would be capable with mechanical and electrical engineering, along with enough software engineering to implement both.”
An alternative approach can be found in Deloitte’s use of job canvases. “An example job canvas is split into columns: One for core competencies for the role, two columns for skills or programs expected but which may increase or decrease in importance for the role, and a fourth column specifically dedicated to skills the company anticipates will be necessary for the role in the future.”
How might a job canvas look for a manufacturing engineer position? “The first column may look similar to a traditional job posting…[listing] technical writing, systems knowledge, and product engineering.” “But the last column gives a blueprint for at least how the company expects the role to evolve — in this case, the theoretical manufacturing engineer should expect to later become skilled in data driven decision making, digital twins, and robotics.”
As companies continue to struggle to hire the highly skilled workers they need for a modern industrial workplace that’s more automated than ever, it’s important to remember that there’s yet another approach that companies can take. Look for candidates with industry-standard credentials that prove they already possess the advanced automation skills needed to thrive. For example, if workers possess a certification from the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), employers can feel confident they’ve already proven they have the knowledge and hands-on skills needed for working with advanced smart automation technologies. SACA has been hard at work collaborating with industry leaders to develop a wide variety of industry-standard certifications that will help employers find workers who possess the advanced connected-systems skills they need to take their businesses to the next level. Be sure to check out SACA and all it has to offer!
- Published in News
Risk Assessment Still Essential to Ensure Cobot Safety
As advanced automation technologies have become commonplace in industrial workplaces over the last decade, many workers have feared that their jobs would soon be replaced by these technologies, such as robots. However, while some dangerous, overly-repetitive job tasks have been taken over by industrial robots, these technologies have actually created a variety of new jobs centered on their installation, operation, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Moreover, many workers now find themselves working right alongside robots that make their jobs easier and safer. These robots, known as collaborative robots or cobots, tend to be smaller, slower-moving versions of their industrial robot counterparts.
Cobots are designed to operate at slower speeds and with more safeguards than traditional robots, so that they can safely operate in close proximity to human workers. Despite these design considerations and the safety record of cobots, experts argue that ongoing risk assessment remains essential to ensure cobots and human workers continue to work safely together.
According to a recent Automation World article by David Greenfield, “beyond the built-in safety aspects of cobots—such as smooth, rounded edges to minimize pinch points, slow operating speeds and lighter load capacities—key safety regulations have been introduced to help ensure a safe working environment.”
For example, “ISO/TS15066 clearly calls out that a risk assessment is necessary to identify the hazards and risks associated with a collaborative robot system application. It notes that the integrator ‘shall conduct a risk assessment as described by ISO 10218 and ANSI/RIA15.06’.”
Risk assessment of automated industrial applications seems like a no-brainer, right? Unfortunately, “cobot risk assessments are commonly overlooked in industry.” Why? Probably because “[t]heir use in industry over the past 10+ years has proven their ability to be used safely.”
According to Greenfield, “[t]ypical application hazards, such as impact questions, trapping and projectiles are often overlooked once the term collaborative robot is used because it’s taken that this is a safe piece of equipment. But this is why a risk assessment is required. So you have to look at the loads, the materials and the robot torque.”
It’s also important to assess risk “related to the cobot’s location. Based on where the cobot is located, you have to consider if you are creating a crushing or a trapping hazard with the cobot. You also have to consider if the cobot position is high enough that it could come into contact with an operator’s head.”
“The bottom line for cobot safety is to: 1) Not assume it will always be safe to use alongside humans just because it’s a cobot; and 2) Identify the hazards and risks associated with your planned use of the cobot using the available safety standards.”
Does your organization use cobots in the workplace? If so, do you have risk assessment procedures in place to ensure worker safety? These types of questions are why it’s critical for industries to hire highly skilled workers that can manage risks, in addition to operating, maintaining, troubleshooting, and repairing the advanced automation systems that are being implemented.
Unfortunately, due to the ongoing “skills gap” issue facing industries across the country, finding highly skilled workers remains a significant challenge. How can employers find the workers they need? And how can they be sure that workers have the hands-on skills they need to succeed in the modern workplace? Today, more and more employers are looking for workers with industry-standard certifications that prove they have the skills needed.
For example, if workers possess a certification from the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA), employers can feel confident they’ve already proven they have the knowledge and hands-on skills needed for working with advanced smart automation technologies. SACA has been hard at work collaborating with industry leaders to develop a wide variety of industry-standard certifications that will help employers find workers who possess the advanced connected-systems skills they need to take their businesses to the next level. Be sure to check out SACA and all it has to offer!
- Published in News
Do Your Students Have the Skills They Need to Succeed in the Workplace of Today and Tomorrow?
How do you shop today? Today’s consumers probably don’t give it much thought, but the ways in which we learn about, shop for, purchase, and ultimately receive the products we want and need has undergone a seismic shift in the last few decades.
Once upon a time, people might have learned about a product by seeing it on a store shelf or in a paper catalog. Today, catalogs tend to be hard to find and many people accomplish most of their shopping without ever entering a brick-and-mortar store.
Instead, the Internet offers instant gratification at your fingertips. A quick search, a few clicks or taps, and all sorts of things you never knew you needed will appear on your doorstep in just a day or two. In fact, the rise of e-commerce has shifted the landscape of the modern workplace, replacing retail jobs with new opportunities in warehouses and fulfillment centers.
These modern jobs continue to evolve as employers grapple with a shortage of skilled workers and the implementation of advanced automation technologies. Today’s instructors responsible for preparing the next generation of workers must take a hard look at whether or not their students have the skills they need to succeed in the workplace of today and tomorrow.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the opportunities available in the modern e-commerce workplace, the effect of advanced automation technologies, the skills future workers will need, and how the Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) can help instructors ensure they’re setting up their students for success.
The Future of Work is Here
Today’s students will find that the modern world of e-commerce offers a wealth of opportunities, mostly with companies that have become household names. While working in a warehouse or fulfillment center might not sound like it’s on the cutting edge, many students will be surprised to learn what exciting career paths these places offer.
If you think about it, a lot has to happen for you to pick up your phone, order a product via an app, and have that product delivered to your home in a matter of only a day or two. The logistics underlying the modern supply chain are both impressive and challenging.
In an Industry Today article, author Carl Schweihs puts it this way:
“It’s no secret that technology is changing the way warehouses work. From robots and cobots that can do repetitive work to artificial intelligence, machine learning, and internet-connected devices that improve the ability to produce products, track productivity and identify maintenance needs, automation is no longer the future – it is the present. More warehouse leaders look to integrate technology into their operations each day. A 2021 survey of manufacturers by industrial staffing firms Staff Management | SMX and SIMOS Solutions showed that more than half were looking to automate parts of the facility in the next five years, with one-quarter planning to implement new technology as soon as possible.”
With continuing problems finding enough skilled workers to fill all of the open positions, it’s no wonder that companies are looking to advanced automation technologies to keep up with the pace of progress. Some people believe this means robots will take all the jobs in the future, but experts disagree.
Robots: It’s Not Us vs. Them
When you hear about companies implementing advanced automation technologies, it can be easy to jump to the conclusion that human workers are losing their jobs and being replaced by machines. However, according to Schweihs, “[t]he idea that robots will ultimately end up replacing people is a false dichotomy that simply isn’t backed up by data.”
In fact, Schweihs believes that “[t]he future of warehouse work won’t be people versus machines, but people and machines.” As advanced automation technologies take over repetitive, dangerous work, human workers will be tasked with more complex tasks that will ultimately provide greater job satisfaction.
In his article, he notes that “adding technology shouldn’t mean removing jobs. Instead of focusing on what robots can do, companies need to think about what their people can do – and how they can make the most impact by working with new technologies.”
What we will see as companies implement these new technologies is a shift in the types of jobs humans will do, as well as the skills they will need to do those jobs. Schweihs notes:
“In the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs 2020 report, 43% of businesses surveyed planned to move toward technology that will replace jobs, but the report showed that those moves could create up to 97 million new roles…Technology will be essential, but so will people. The only difference is that they will no longer be doing only step-by-step work to move a product from one end of the warehouse to another.”
Future Workers Need Different Skills
The workplace of the future – and in many cases, the present – will require workers with different skills than they’ve previously needed. Schweihs sees a future in which workers “will be skilled in both working with technology and in more intricate processes and functions.”
“From expertise in systems and processes to complex tasks, companies need people who can make decisions and perform work that technology can’t handle. And because no automated system can be online 100 percent of the time, actual humans will be there to pick up the slack,” insists Schweihs.
Schweihs believes “the jobs of the future will continue to evolve into more complex work that will improve both output and productivity. Future warehouse jobs will be a mix of complex tasks assisted by technology, existing roles supplemented by technology, and new jobs that will help with output and production.” One thing is clear: in the warehouses and fulfillment centers of the present and future, connected systems skills will be more important than ever.
Unfortunately, many instructors feel overwhelmed with the prospect of preparing their students with these new skills their students will need to succeed in the future workplace. What skills should they teach, and how will their students prove to prospective employers that they possess the skills that will let them hit the ground running? The answer to these questions can be found in the smart automation certifications offered by the Smart Automation Certification Alliance.
SACA Certifications Outline Clear Pathways for Student Success
As Schweihs notes in his article, “[t]he jobs of the future are coming, but it pays to get started now…The warehouse of the future is not simply a dark cavern full of machines. It will be a lively place with workers using the knowledge and skills they learn…to ensure that any technology added to the workflow is working well and serving everyone’s needs.”
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance sits at the forefront of the effort to certify students who demonstrate the required knowledge and hands-on smart automation skills employers so desperately need. SACA provides a wide variety of certifications that ensure future workers have the connected systems skills employers require.
To learn more about advanced automation certifications and how SACA can help educational institutions begin the task of bridging the Industry 4.0 skills gap, instructors should contact SACA for more information. The process begins by forging partnerships with local industries to determine the types of jobs they need to fill and what skills those roles require.
With a solid industry-education partnership forming the foundation of your effort to create new career pathways for your students, you can then choose the right credentials to validate the skills employers are seeking. Fortunately, you don’t have to recreate the wheel.
SACA offers many credentials to facilitate career pathways to successful new careers for students. For example, here are just a few of the subject matter areas in which SACA offers credentials: electrical, motor control, programmable controllers, mechanical, pneumatics, hydraulics, automation, Industry 4.0 technologies, robotics, electronic sensors, smart factory operations, process control, Ethernet communications, networking, data analytics, and predictive maintenance.
- Published in News
Identifying specialists within the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Supply chain issues persist within the global manufacturing industry. Although nimble companies have found ways to navigate the issues brought about by COVID19, experts still anticipate concerns continuing through 2022, caused by the lingering effects of the pandemic and other global events.

One of the most pervasive issues stems from the reality that domestic manufacturing relies heavily on components made in other countries. While efforts are being made to mend this, in particular attempts to re-instate the component manufacturing industry in the US, it’s clear that this industry will reemerge in a different way with a focus on mechanization and automation.
The foundation of a long term strategy to mitigate these problems in the future will involve leveraging the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which presents a groundbreaking opportunity for data capture at each step of a manufacturing process.
This extensive study by Inmarsat indicates that many manufacturing companies are either already using or anticipate using IIoT to enhance their productivity. A smart factory can track all elements of the production chain and communicate information and even anticipations within the network.

In addition to valuably capturing data, a smart-automation chain can perform pre-emptive actions based on the needs of the incoming workload; for example submitting a work-order for components required on the production line, utilizing a company’s secure industrial WLAN.
Unlike residential (or office) WiFi, an industrial system transfers small amounts of data, and as such requires a small amount of power but must remain uninterrupted. Knowledge of the specificities of these systems is essential to optimize an efficient order-to-customer pipeline.
Because of innovations like re-programmable robots and even rent-a-bot companies emerging, there is much less danger of expensive built-in obsolescence and more opportunity for network, automation and programming specialists within manufacturing companies.
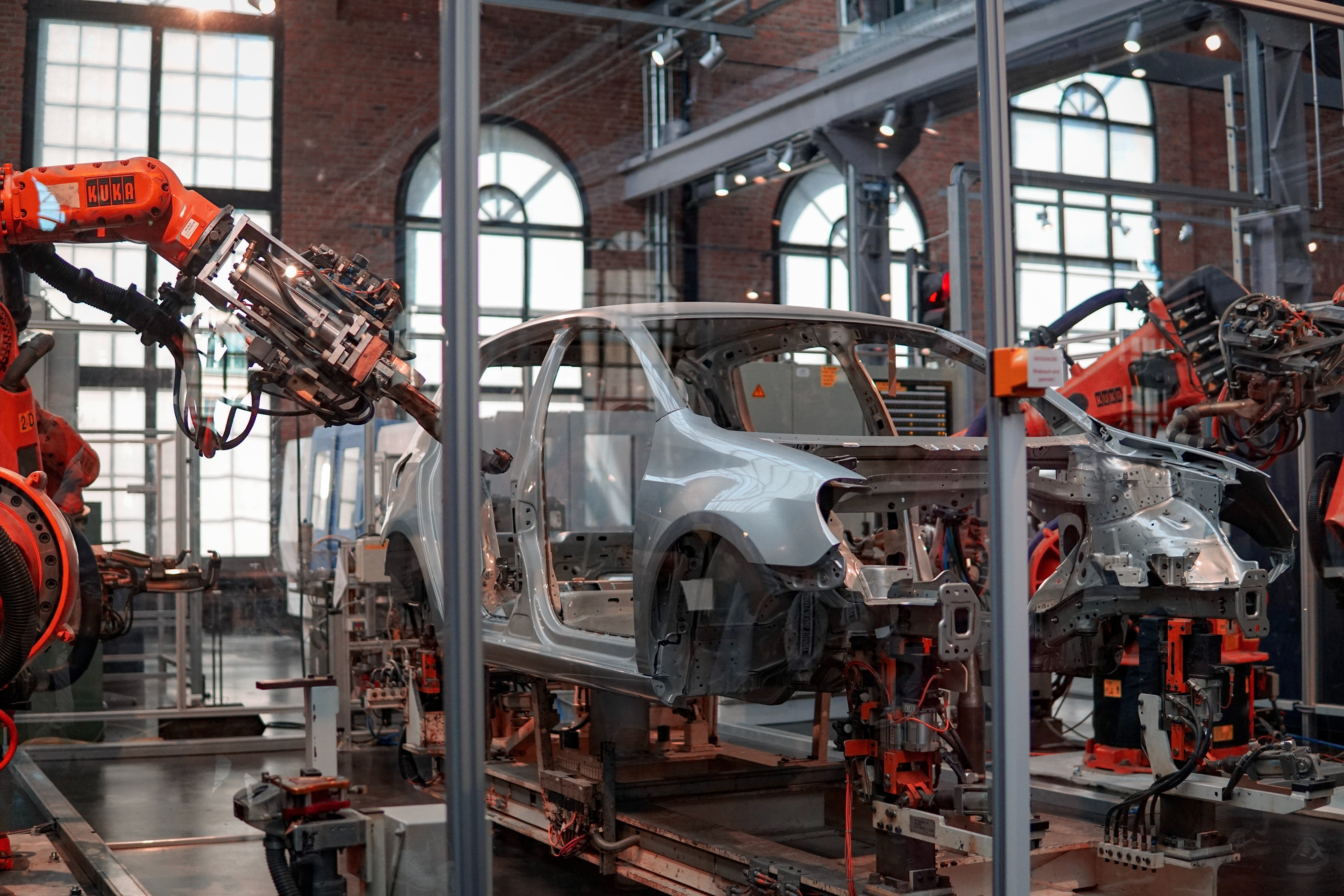

Companies searching for highly-skilled workers to ease their supply chain disruptions want to make sure that potential employees actually have the skills to excel without significant additional training. That’s why industry-standard certifications are important for supply chain workers. They provide employers with evidence that a worker has the knowledge and hands-on skills to work with today’s advanced technologies.
Industrytoday.com states that ‘new developments in automation are allowing small manufacturers to meet demand while helping with American competitiveness’. Today’s workers need more advanced technical and technological skills than ever before. Unfortunately, there aren’t enough workers with these skills to fill the many roles available today, creating what is known throughout industry as the “skills gap.” Modern businesses must ensure that their workers have up-to-date, relevant accredited skills. How can companies be sure that their employees are at the correct skill-level?
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) focuses on connected-systems skills and leads the effort to certify students and workers who demonstrate the required knowledge and hands-on smart automation skills employers so desperately need. SACA professional development opportunities provide extensive training courses to equip teachers to promote Industry 4.0 certifications. These professional development opportunities are offered throughout the year at regional centers. Courses last 3-5 days each. Upon successful completion of each course, teachers will be certified in the process of examining students for a given credential and administrating a certification preparation course.
To learn more about Industry 4.0 certifications and how SACA can help both educational institutions and industry employers begin the task of bridging the Industry 4.0 skills gap, contact SACA for more information.
Header Photo by Denny Müller on Unsplash
- Published in News
Are Cobots the Future of Automation in Manufacturing?
As 2022 begins, leaders of manufacturing companies across the country and around the globe are looking for solutions to a wide variety of challenges. Between the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and a critical shortage of highly-skilled workers, manufacturers have their work cut out for them.
Increasingly, manufacturers are turning to advanced automation technologies to solve the problems they face. Adding these technologies can allow manufacturers to optimize processes to meet production deadlines more effectively and efficiently.
When many people hear the phrase “advanced automation technologies,” they often immediately think of robots. Industrial robots certainly do play an important role in many modern manufacturing facilities. However, some companies cannot afford large-scale implementation of expensive robots. Moreover, current workers worry that their jobs will be replaced by machines, leaving them unemployed and searching for new opportunities.
The rise of a new advanced automation technology — the collaborative robot or “cobot” — may offer manufacturers of all sizes new opportunities to automate processes while not only keeping their current employees, but also making their work lives better and more satisfying. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at cobots, their advantages over traditional industrial robots, and their potential applications in manufacturing facilities.
What are Cobots?
Traditional industrial robots tend to be large machines tasked with dangerous, repetitive jobs. Their size and movements present a potential source of danger to employees, so they’re usually cordoned off from employees for safety purposes.
Collaborative robots — also known as cobots — represent a new generation of machine designed to work safely alongside humans in the manufacturing environment. Rather than being cordoned off like traditional robots, cobots tend to be smaller so they can share space with human workers, a significant benefit in facilities with limited space.
Advanced safety features allow cobots to work effectively in close proximity to human workers. While cobots take over repetitive tasks, their human counterparts are freed up to focus on more complex tasks that involve troubleshooting or problem solving.
In fact, far from replacing human workers, cobots often rely on them to lead by example. In a Tech Briefs article, author Megan R. Nichols notes:
“Instead of relying on a programmer to tell them what to do, cobots are often taught by example. An operator physically controls the bot’s movements, running it through its necessary tasks. The cobot can then remember which tasks it needs to complete and perform them again and again with perfect recall and execution.”
How are Cobots Different from Traditional Industrial Robots?
Cobots are growing in popularity throughout the manufacturing sector. In an Interesting Engineering article, author Susan Fourtané reports that experts are forecasting annual global revenues of cobots to be between $7.6 billion and $9.2 billion within the next three to five years.
Why are cobots growing in popularity so rapidly? The answer lies in some of the unique benefits they provide that separate them from traditional industrial robots. According to Fourtané:
“Many believe human and machine collaboration plays a paramount role in the development of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)…The characteristics of collaborative industrial robots suit the demands of Industry 4.0 and the global megatrends better than those of traditional industrial robots. In other words, cobots are better equipped to join humans in Industry 4.0 — also called the Fourth Industrial Revolution — than traditional industrial robots.”
Here are a few of the key differences between cobots and traditional industrial robots:
Flexibility
Traditional industrial robots tend to be large, powerful machines that require a fixed installation dedicated to a single task. Cobots, on the other hand, are usually smaller, allowing for easy relocation and efficient task changes.
According to a Techman Robot Inc. blog post, “Some cobots are even made to be mobile, so you can easily transfer them to help out another station. They operate much more straightforward than their industrial counterparts, which need extensive changes done to their software and hardware to be repurposed.”
Versatility
Not only are cobots more compact and slower than traditional industrial robots, they’re also easier to use for a variety of tasks. For example, the Techman Robot Inc. blog post notes:
“Cobots are designed to take on different kinds of tasks. As long as you have the suitable end effectors, you can program packing bots to take on labeling or inspecting jobs in just a few minutes.”
Ease of Setup
Whereas a traditional industrial robot can take months to install and usually requires an expert to program, cobots often require little to no programming experience to set up. Even the most modest manufacturing facilities can implement cobots and train workers to use them in a matter of weeks.
Cobots feature the added benefit of empowering their human counterparts. Not only do cobots take over manual, repetitive tasks that would otherwise put humans at risk of injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome and back pain, but they also allow human workers to dedicate their time to more creative, fulfilling tasks, thereby improving job satisfaction and worker morale.
Cost
Given their smaller size and ease of use, it should come as no surprise that cobots are less expensive than traditional industrial robots. A lower price tag combined with their ease of setup, versatility, and flexibility makes cobots an attractive option for adding advanced automation capabilities to any size manufacturing facility.
As Nichols concludes in her article:
“Cobots may never fully replace traditional robots for large-scale manufacturing projects that require speed and power. The robots, however, will be the perfect tools to take over the repetitive entry-level tasks that are a part of many industries. If you design a robot that can handle these tasks, your skilled workers can spend their energy on other, more crucial tasks.”
What Applications do Cobots have in Manufacturing?
The unique benefits of cobots that set them apart from traditional industrial robots make them an attractive option for many different types of manufacturing facilities. But are they good for all applications? In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the manufacturing applications particularly suited to cobots.
In a Forbes article, author Naveen Joshi notes that cobots are “[o]ne of the most extensively used types of automation machines” and that, “[a]s the underlying technologies mature, collaborative robots in manufacturing can be made more versatile to take up more creative tasks.” The article highlights five key applications of cobots in manufacturing:
Picking, Packing, & Palletizing
Cobots equipped with cameras can accurately and efficiently pick, pack, and palletize a wide variety of products. Adding grippers or suction cups allows cobots to create cartons, pack items, and seal boxes, making fulfillment much easier.
Welding
The Techman Robot Inc. blog post notes that “[c]obots are so accurate that companies are using them to handle process tasks like soldering, screwing, and welding. They can perform these tasks day in and day out (and even after hours) without any slow-downs. They make little to no mistakes, too, so you can rest easy knowing your products have consistently good quality.”
Assembly
According to an Association for Advancing Automation article, cobots “are effective at automating [tedious and physically-demanding] tasks, like holding heavy parts, to allow human workers to be more productive with less risk of injury.” They’re also “more flexible than industrial robots. They can be integrated and programmed far quicker and with greater ease. This makes them more profitable in environments where the robot has to conduct various different tasks.”
Material Handling
Cobots come in mobile versions that can carry materials via a specific route. Not only can they handle hazardous materials safely, but they also streamline processes by eliminating the need for human workers to carry heavy boxes or use heavy equipment, such as forklifts.
Inspection/Quality
According to the Techman Robot Inc. blog post, “[c]obots can be equipped with cameras or sensors that inspect parts of a product for any defects. They can also be used to measure specific components to ensure that they’re being sorted into the right stream in the assembly line.”
Contact SACA to Learn More about Smart Automation Certifications
Cobots are just one of the many forms of new advanced, “connected” technologies that characterize what’s commonly known as Industry 4.0. These technologies, as a group, also go by a variety of monikers, including Smart Factory and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Today’s workers need more advanced technical and technological skills than ever before. Unfortunately, there aren’t enough workers with these skills to fill the many roles available today, creating what is known throughout industry as the “skills gap.”
How can modern businesses find the workers they need? How will educational institutions teach the skills modern industry needs? These are questions that demand answers, and one promising solution is the development of industry-standard certifications that focus on connected-systems skills. The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) sits at the forefront of the effort to certify students and workers who demonstrate the required knowledge and hands-on smart automation skills employers so desperately need. To learn more about Industry 4.0 certifications and how SACA can help both educational institutions and industry employers begin the task of bridging the Industry 4.0 skills gap, contact SACA for more information.
- Published in News