Smartphones, Smartwatches, & Now Smart…Factories?
Did you ever have math teachers who were real sticklers for knowing the fundamentals? Frequent reminders to “show your work” were likely accompanied by the admonition that “you’re not always going to have a calculator in your pocket!”
Well, I guess we showed them didn’t we? The smartphones that occupy our pockets today not only have a calculator, a telephone, a calendar, a map, an address book, a clock, a camera, and a music player, they also contain a nearly-limitless variety of applications that give us access to data and capabilities unimaginable a generation ago.
Your smartphone might connect to a smartwatch that keeps track of your heart rate while you read emails on the go. It might also connect to a variety of smart home devices, allowing you to turn on light bulbs, answer the doorbell, and lower the thermostat from anywhere in the world.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
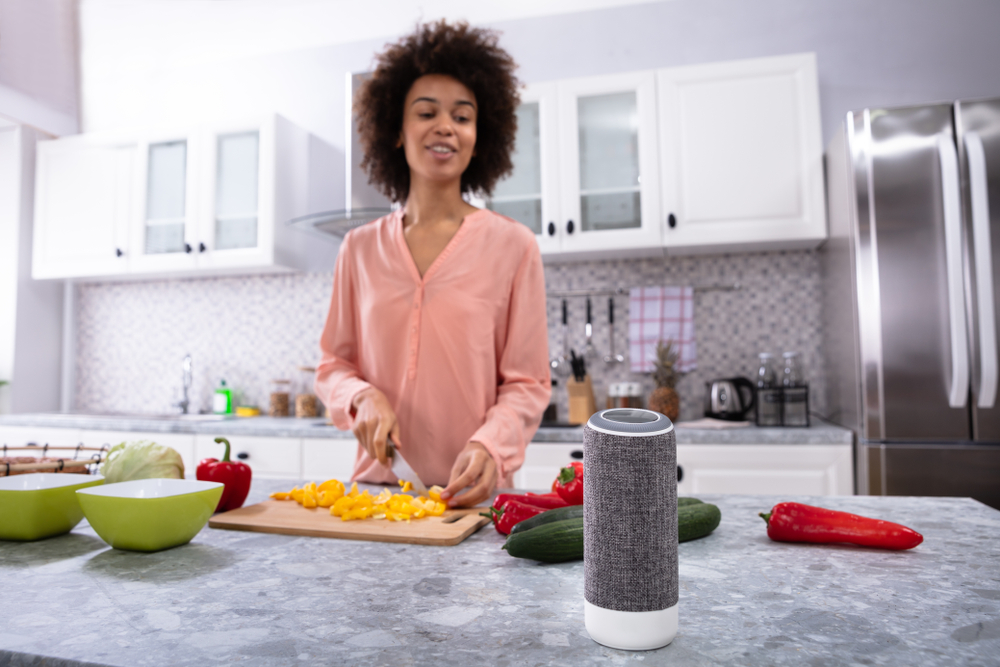

All of these so-called “smart” devices are part of what’s now known as the “Internet of Things” (IoT). The IoT allows a wide variety of devices to connect and communicate using the Internet, making life more convenient in ways many people never dreamed possible.
There are now even voice-activated assistants ready to do our bidding. Today, a call of “Hey Siri!” or “Hey Alexa!” might be followed by a command to turn on the outside lights at home, an inquiry about the state capital of Wisconsin (it’s Madison, by the way), a request for the latest weather forecast, or an appeal for a quick eggs Benedict recipe.
Our lives have been forever transformed by the IoT. Today’s youth have grown up in a world of connected devices. Even older adults, though, now use these devices and understand their benefits. Many of us see how they make our day-to-day lives easier, but do we fully realize how they will impact our jobs, both now and into the future?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
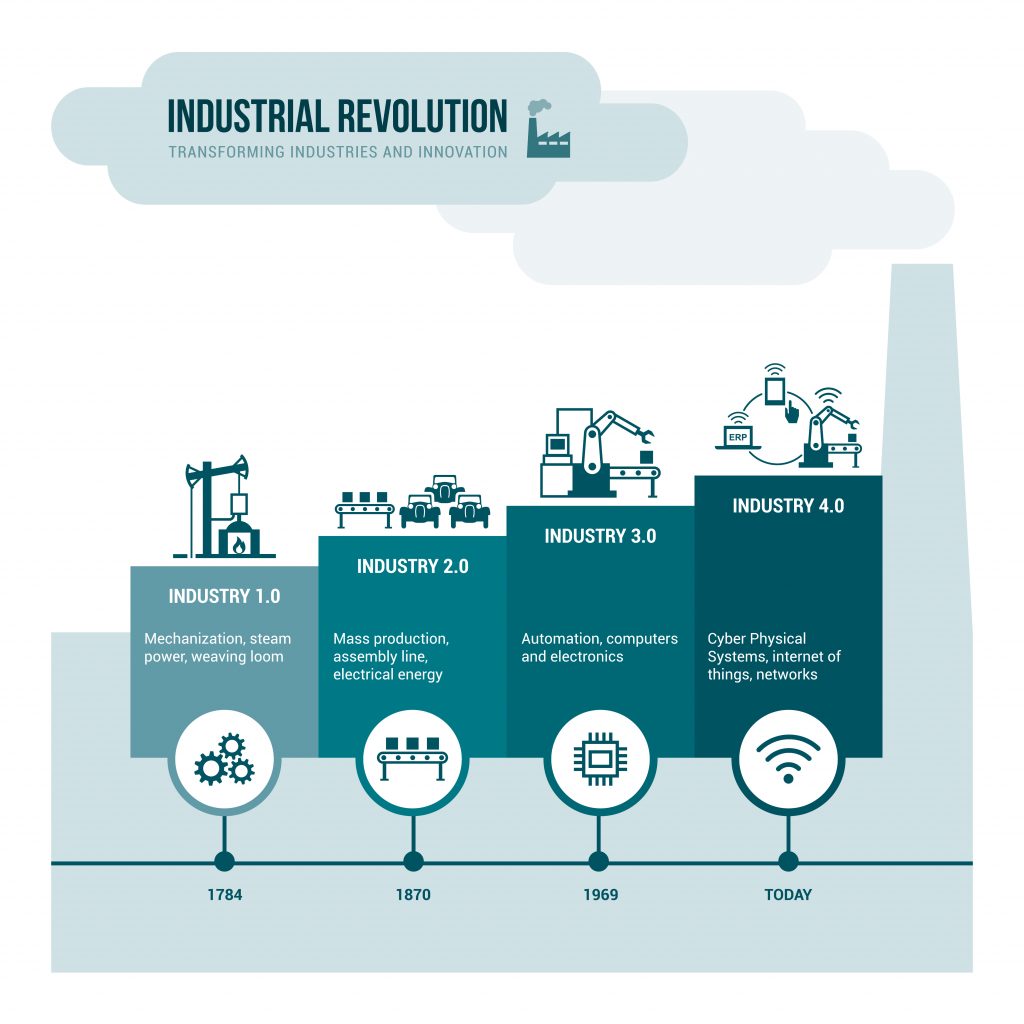
History buffs will remember that the Industrial Revolution began in the second half of the 18th century when manpower began to be replaced by machines powered by steam or coal. What many people don’t realize, however, is that scholars have identified subsequent revolutions in industry.
The Second Industrial Revolution got its start in the first half of the 19th century when electricity combined with the assembly line to allow mass production. A Third Industrial Revolution traces its roots to the 1950s when the digital age was born with the advent of the first computers and the beginnings of automation.
Today, we find ourselves in the early stages of the Fourth Industrial Revolution when cyber-physical systems, automation, and the IoT will combine to create a Smart Factory environment that holds the potential for a massive impact on industrial efficiency and productivity.
Whatchamacallit
This new Fourth Industrial Revolution goes by a variety of names and terms: Smart Automation, Smart Factory, Smart Manufacturing, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the Industrial Internet, the Connected Enterprise, and Industry 4.0, to name a few. Whatever you choose to call it, it’s both the wave of the future and the present reality.

Smart factories already exist, and they’re getting bigger and better every day. Industry 4.0 pioneers in a wide variety of industries are forcing competitors to embrace Smart Automation as a tool to take them to the next level.
Inside the Smart Factory
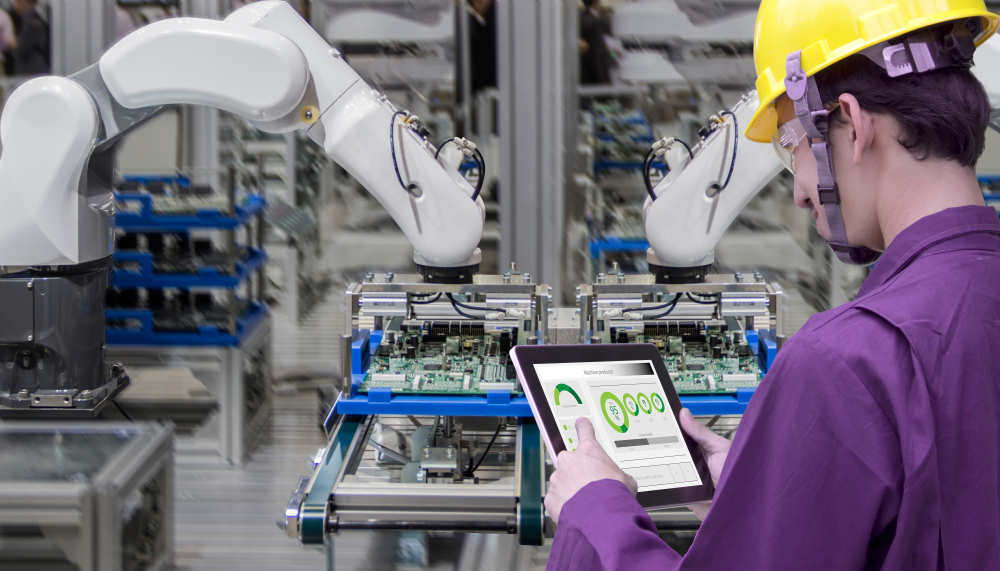

What is a Smart Factory like? Envision a facility in which self-driving vehicles communicate with production-line robots to request and deliver necessary parts without human intervention. Imagine these connected machines on the production floor communicating with workers on the top floor to convey a wide variety of information, such as production cycle times, mechanical breakdowns, and predictive maintenance.
Smart robots and machines equipped with smart sensors can generate a virtually-unlimited amount of data (often referred to as “big data”) that can be shared with multiple locations via cloud technology. This data can be used not only to monitor real-time production status but also to predict future maintenance needs. Can you imagine a robot continually analyzing its productivity and condition, so it can order replacement parts or other maintenance needs before it breaks down?
The Skills Gap

At one time, many workers feared the day when robots would replace humans in the workplace. Some still do. However, the reality of Industry 4.0 is quite different. While it’s true that robots and automated machines have replaced some jobs, the advanced technologies required by Industry 4.0 have and will continue to generate a tremendous demand for highly-skilled workers to program, analyze, and maintain the many parts of these complex systems.
That sounds fantastic until you realize that industry experts believe there’s a tremendous shortage of workers qualified to fill these positions. According to a recent study by Deloitte, nearly 3.5 million manufacturing jobs will need to be filled in the next decade. Because of what is commonly known as the “skills gap,” however, experts estimate as many as 2 million of those jobs could go unfilled.
Training for a New World

Despite the fact that we live in a connected world and understand its benefits, many people still lack the skills they will need to thrive in an Industry 4.0 environment. While many people have embraced advanced technology in their personal lives, they lack real-world exposure to manufacturing equipment and processes.
To prepare students and current workers for careers in smart factories, educators and companies must teach skills in a variety of areas, including industrial equipment and technology, smart sensors and smart devices, computerized control systems, network security, and data collection and analysis. Experience with real-world equipment and access to state-of-the-art training will be critical.
SACA’s Vision

Once you gain experience and receive the training you need, how will you market yourself to employers? How can you easily demonstrate to others the skills, experience, and training that you possess?
The Smart Automation Certification Alliance (SACA) offers highly-affordable, accessible Industry 4.0 certifications for a wide range of industries. While many certifications are available today that address isolated competencies, from welding and machining to maintenance and IT, SACA certifications are different. They certify “connected systems” skills that address the integration of these technologies with Industry 4.0 technology.
SACA’s vision is to provide certifications that significantly increase the number of individuals who possess the skills represented by these credentials. This will ensure that companies have the highly-skilled workers they need, and individuals are prepared to be successful in Smart Factory jobs that require certified “connected systems” skills.
- Published in News